Concept design report
One of the outputs of the concept design stage is to produce a report which records the design concepts for major aspects of the project that might be worth developing as detailed designs. The report also identifies instructions required from the client.
The concept design report might include:
- The aims and objectives of project.
- A summary of the project brief.
- Areas of compliance and divergence between the concept design and the project brief.
- Identification of constraints, including local context, site levels, access, buildability, manufacturing, financial and local authority planning and building regulations.
- The outcome of key consultations.
- Statement of how the design meets the client's needs.
- Site context and strategy.
- Design and access statement.
- Site layout, including car parking, hard surfaces, water features, art etc.
- Landscape strategy.
- Layout of accommodation, including analysis of adjacencies between functions.
- Sections.
- Elevations.
- 3D visualisations and/or physical models.
- Fire strategy.
- Services strategy including emissions targets.
- Information and communications technology (ICT) strategy.
- Maintenance strategy.
- Quality standards.
- Materials.
- Definition of key construction elements, standardisation and non standard elements.
- Prefabrication and mass production opportunities.
- Long-lead items.
- Proposals for major engineered systems such as: cladding, mechanical and electrical equipment, lifts, and structural frames.
- Potential requirement for specialist design.
- Outline proposals for structural systems and where appropriate method of demolition.
- Outline proposals for building services systems.
- Schedules of accommodation.
- Planning strategy.
- Soft landings strategy.
- Cost plan, providing a break-down of the capital and ‘life cycle’ costs and identifying potential cost problems and cost reduction possibilities.
- Procurement options such as two-stage tendering.
- Programme and phasing.
- Buildability and construction logistics.
- The use of materials and the potential for re-use and recycling.
- Waste handling (see also site waste management plan).
- Sustainability.
- Risk assessment.
- Health and safety issues.
- Areas requiring further research.
- Instructions required.
The concept design report should only include required, or key co-ordinated information and necessary interpretation and should not duplicate information that already exists elsewhere.
Where building information modelling (BIM) is being used, publication of the concept design report may be part of a 'data drop' or 'information exchange' intended to ensure the project is properly validated and controlled as it develops. This may include:
- Models (Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) models and native project information models).
- Data structures (such as COBie files and schedules).
- Reports (typically PDF’s, although native files can be more useable).
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Concept design.
- Concept architectural design.
- Concept architectural design checklist
- Concept services design.
- Concept structural design.
- Constraints.
- Data drop.
- Design and access statement.
- Design methodology.
- Design phase.
- Detailed design.
- Detailed design report.
- End of stage report.
- Gateways.
- Outline planning permission.
- Outline specification.
- Project brief.
- Site waste management plan.
- Soft landings.
- Stage 2 design report.
- Sustainability.
Featured articles and news
Tackle the decline in Welsh electrical apprenticeships
ECA calls on political parties 100 days to the Senedd elections.
Resident engagement as the key to successful retrofits
Retrofit is about people, not just buildings, from early starts to beyond handover.
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
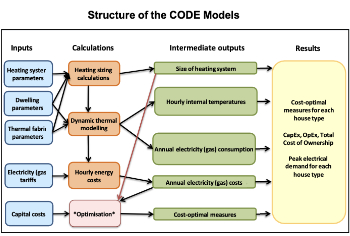
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.





















Comments